 CIDC - Measured Variable Atmospheric Constituents
CIDC - Measured Variable Atmospheric Constituents CIDC - Measured Variable Atmospheric Constituents
CIDC - Measured Variable Atmospheric Constituents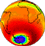 Ozone from TOMS
Ozone from TOMS
Precise records of past and present atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4)
and nitrous oxide (N2O) concentrations are critical to studies attempting to understand
the effects these gases have on climate change. Researchers have attempted to determine past levels of
the atmospheric gases by a variety of techniques, including direct measurements of trapped air in polar
ice cores, indirect determinations from carbon isotopes in tree rings, analysis of spectroscopic data,
and measurements of carbon and oxygen isotopic changes in carbon sediments in deep-ocean cores. The
modern period of precise atmospheric measurements began during the International Geophysical Year (1958)
with Keeling's (Scripps Institution of Oceanography) pioneering determinations at Mauna Loa, Hawaii
and at the South Pole. Since that time the number of sites that measure atmospheric gases has grown to
over sixty sites on both the land surface and ocean.  Greenhouse Gases from CDIAC
Greenhouse Gases from CDIAC
This dataset describes Atmospheric Chemistry records and isotope temperature records acquired from the Carbon
Dioxide Information Analysis Center (CDIAC) Trends '93: A Compendium of Data on Global Change. Trends '93
is part of CDIAC continuing effort to distribute, in an accessible format, scientific data critical
to global-change issues.
This subset of the Trends '93 collection includes the following:
Readers may note that two apparently different systems of units have been used in presenting the
atmospheric data. For data from ice cores and for some modern atmospheric records, levels are presented
as concentrations in parts per million by volume (ppmv). For much of the modern data, values are given
as mixing ratios, in parts per million or in parts per million by volume. These differences in unit
designations reflect the preferences of the researchers who have contributed their respective data
sets for inclusion in Trends '93. In the context of atmospheric concentration in parts per million by
volume refers to the number of volumes of the particular gas (CO2, CH4 and
N2O) per million volumes of sample. In this same context, mixing ratio in parts per million
is derived by dividing the number of moles of the particular gas (CO2, CH4 and
N2O) by the total number of moles in the sample and then multiplying the quotient by one
million. Assuming that the volume of a gas is proportional to the number of moles contained within
the volume (this assumption should be valid for a gas (CO2, CH4 and
N2O) in air under the conditions that atmospheric measurements are routinely carried out),
we can expect that a gas (CO2, CH4 and
N2O) concentrations should be equivalent to the same gases mixing ratios. For all practical
applications, therefore, users of this data should consider the terms concentration and mixing ratio
to be interchangeable.