 CIDC - The Biosphere
CIDC - The Biosphere CIDC - The Biosphere
CIDC - The Biosphere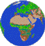 Vegetation Index from AVHRR NDVI
Vegetation Index from AVHRR NDVI
This dataset is a collection of monthly composites of ocean chlorophyll concentration derived from the
Coastal Zone Colour Scanner (CZCS) instrument flown aboard the Nimbus-7 satellite from October 1978
through June 1986. This concentration provides a direct measure of the abundance of phytoplankton and
its variability in space and time over most of the world's oceanic regions. The CZCS dataset represents
the only source of satellite-derived, global oceanic biomass productivity, and serves as an important
precursor to the next generation of advanced ocean colour instruments (
Feldman et al., 1989). These include the Sea-Viewing
Wide Field-of-View Sensor (SeaWiFS), launched on August 1, 1997, and future missions conducted as part of
NASA's Mission to Planet Earth program.
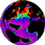 Ocean Pigment Concentration from CZCS
Ocean Pigment Concentration from CZCS
Land cover is described in terms of 13 vegetation types plus water, ice and bare desert soil. Phenological
differences among vegetation types, reflected in temporal variations in NDVI derived from
satellite data, have been used to classify land cover at continental scales. This study explored
methodologies for extending this concept to a global scale (DeFries and
Townshend 1994a). A coarse
resolution (1° x 1°) dataset of monthly NDVI values for 1987 (Los et al.
1994, Sellers, et al.
1994, 1995b) was used as the basis for a supervised
classification of eleven cover types that broadly
represent the major biomes of the world. Because of missing values at high latitudes, the Pathfinder
AVHRR dataset for 1987 (James and Kalluri, 1994) for summer monthly
NDVI and red reflectance values
were used to distinguish the following cover types: tundra, high latitude deciduous forest and woodland,
coniferous evergreen forest and woodland.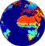 Global Land Cover from ISLSCP
Global Land Cover from ISLSCP
The land cover dataset was further modified to be consistent with the SiB vegetation classes described
in Dorman and Sellers, (1989), Sellers
et. al. (1995a) and Sellers et. al. (1995b). This dataset is
also available on the ISLSCP Initiative I CD-ROM set.